引入
上一篇介绍了经典的 HED 边缘检测模型
这一次继续介绍另一篇边缘检测方向的经典论文:Richer Convolutional Features for Edge Detection
其中提出了一个新的模型 RCF,基于更丰富的卷积特征来进行边缘检测,效果相比 HED 有所提升
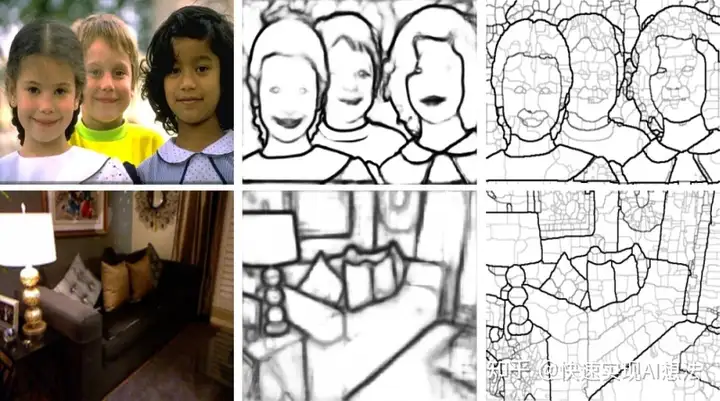
效果演示
RCF 边缘检测
视频演示
更多细节请参考论文/项目主页及代码
参考资料
论文:
Richer Convolutional Features for Edge Detection 项目主页:
Richer Convolutional Features for Edge Detection 官方代码:
yun-liu/rcf
参考引用: @article{RcfEdgePami2019, author = {Yun Liu and Ming-Ming Cheng and Xiaowei Hu and Jia-Wang Bian and Le Zhang and Xiang Bai and Jinhui Tang}, title = {Richer Convolutional Features for Edge Detection}, year = {2019}, journal= {IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell.}, volume={41}, number={8}, pages={1939 - 1946}, doi = {10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2878849}, }
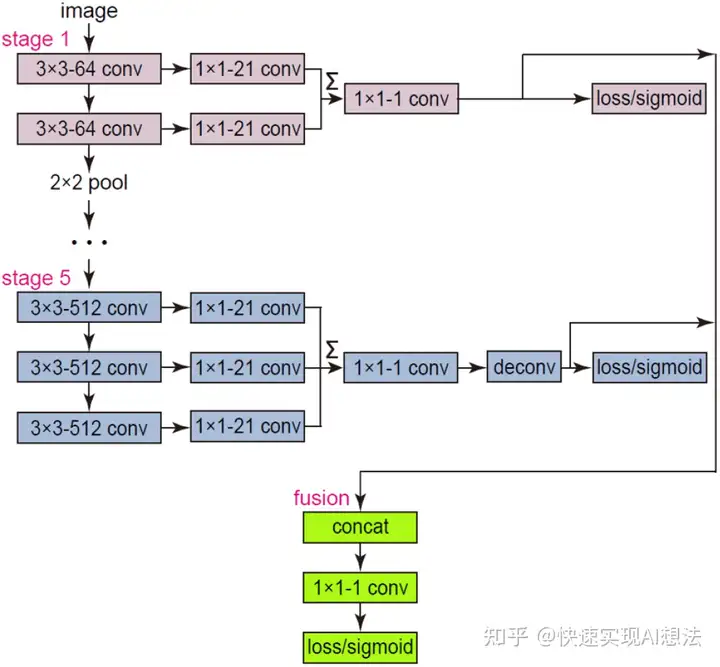
模型架构
RCF 与 HED 模型一样,包含五个层级的特征提取架构,同样也是基于 VGG 16 Backbone
相比 HED,RCF 模型更加充分利用对象的多尺度和多级信息来全面地执行图像到图像的预测
RCF 不只是使用了每个层级的输出,而是使用了每个层级中所有卷积层的输出进行融合(Conv + sum)后,作为边缘检测的输入
模型结构图如下:
代码实现
RCF 的模型架构现在看来其实还算是简单的
接下来就实际的来实现一下
导入必要的库
import paddle
import paddle.nn as nn
import paddle.nn.functional as F
import cv2
import numpy as np
import PIL.Image as Image
VGG16 Backbone
VGG 骨干网络,基于 Paddle.vision 中的 VGG 模型开发而来
import paddle
import paddle.nn as nn
from paddle.utils.download import get_weights_path_from_url
__all__ = []
model_urls = {
vgg16: (https://paddle-hapi.bj.bcebos.com/models/vgg16.pdparams,
89bbffc0f87d260be9b8cdc169c991c4),
vgg19: (https://paddle-hapi.bj.bcebos.com/models/vgg19.pdparams,
23b18bb13d8894f60f54e642be79a0dd)
}
class VGG(nn.Layer):
"""VGG model from
`"Very Deep Convolutional Networks For Large-Scale Image Recognition" <https://arxiv.org/pdf/1409.1556.pdf>`_ Args:
features (nn.Layer): Vgg features create by function make_layers.num_classes (int): Output dim of last fc layer. If num_classes <=0, last fc layer will not be defined. Default: 1000.
with_pool (bool): Use pool before the last three fc layer or not. Default: True. Examples:
.. code-block:: python
from paddle.vision.models import VGG from paddle.vision.models.vgg import make_layers
vgg11_cfg = [64, M, 128, M, 256, 256, M, 512, 512, M, 512, 512, M] features = make_layers(vgg11_cfg)
vgg11 = VGG(features)
"""
def __init__(self, features, return_idx=None):
super(VGG, self).__init__()
self.features = features
self.return_idx = return_idx
def forward(self, x):
outputs = []
for layer in self.features:
x = layer(x)
if isinstance(layer, nn.ReLU):
outputs.append(x)
if self.return_idx is not None:
outputs = self.get_features(outputs, self.return_idx)
return outputs
def get_features(self, outputs, return_idx):
features = []
for idx in return_idx:
if isinstance(idx, list):
_features = self.get_features(outputs, idx)
features.append(_features)
elif isinstance(idx, int):
features.append(outputs[idx])
else:
raise ValueError(return idx is error.)
return features
def make_layers(cfg, batch_norm=False):
layers = []
in_channels = 3
for v in cfg:
if v == M:
layers += [nn.MaxPool2D(kernel_size=2, stride=2)]
else:
conv2d = nn.Conv2D(in_channels, v, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
if batch_norm:
layers += [conv2d, nn.BatchNorm2D(v), nn.ReLU()]
else:
layers += [conv2d, nn.ReLU()]
in_channels = v
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
cfgs = {
A: [ # return_idx
64, # 0
M, 128, # 1
M, 256, 256, # 2, 3
M, 512, 512, # 4, 5
M, 512, 512 # 6, 7
],
B: [ # return_idx
64, 64, # 0, 1
M, 128, 128, # 2, 3
M, 256, 256, # 4, 5
M, 512, 512, # 6, 7
M, 512, 512 # 8, 9
],
D: [ # return_idx
64, 64, # 0, 1
M, 128, 128, # 2, 3
M, 256, 256, 256, # 4, 5, 6
M, 512, 512, 512, # 7, 8, 9
M, 512, 512, 512 # 10, 11, 12
],
E: [ # return_idx
64, 64, # 0, 1
M, 128, 128, # 2, 3
M, 256, 256, 256, 256, # 4, 5, 6, 7
M, 512, 512, 512, 512, # 8, 9, 10, 11
M, 512, 512, 512, 512 # 12, 13, 14, 15
],
}
def _vgg(arch, cfg, batch_norm, pretrained, **kwargs):
model = VGG(make_layers(cfgs[cfg], batch_norm=batch_norm), **kwargs)
if pretrained:
assert arch in model_urls, "{} model do not have a pretrained model now, you should set pretrained=False".format(
arch)
weight_path = get_weights_path_from_url(model_urls[arch][0],
model_urls[arch][1])
param = paddle.load(weight_path)
model.load_dict(param)
return model
def vgg11(pretrained=False, batch_norm=False, **kwargs):
"""VGG 11-layer model
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet. Default: False.batch_norm (bool): If True, returns a model with batch_norm layer. Default: False. Examples:
.. code-block:: python
from paddle.vision.models import vgg11 # build model
model = vgg11()
# build vgg11 model with batch_norm
model = vgg11(batch_norm=True)
"""
model_name = vgg11
if batch_norm:
model_name += (_bn)
return _vgg(model_name, A, batch_norm, pretrained, **kwargs)
def vgg13(pretrained=False, batch_norm=False, **kwargs):
"""VGG 13-layer model
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet. Default: False.batch_norm (bool): If True, returns a model with batch_norm layer. Default: False. Examples:
.. code-block:: python
from paddle.vision.models import vgg13 # build model
model = vgg13()
# build vgg13 model with batch_norm
model = vgg13(batch_norm=True) """
model_name = vgg13
if batch_norm:
model_name += (_bn)
return _vgg(model_name, B, batch_norm, pretrained, **kwargs)
def vgg16(pretrained=False, batch_norm=False, **kwargs):
"""VGG 16-layer model
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet. Default: False.batch_norm (bool): If True, returns a model with batch_norm layer. Default: False. Examples:
.. code-block:: python
from paddle.vision.models import vgg16 # build model
model = vgg16()
# build vgg16 model with batch_norm
model = vgg16(batch_norm=True) """
model_name = vgg16
if batch_norm:
model_name += (_bn)
return _vgg(model_name, D, batch_norm, pretrained, **kwargs)
def vgg19(pretrained=False, batch_norm=False, **kwargs):
"""VGG 19-layer model
Args: pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet. Default: False.
batch_norm (bool): If True, returns a model with batch_norm layer. Default: False. Examples:
.. code-block:: python
from paddle.vision.models import vgg19 # build model
model = vgg19()
# build vgg19 model with batch_norm
model = vgg19(batch_norm=True) """
model_name = vgg19
if batch_norm:
model_name += (_bn)
return _vgg(model_name, E, batch_norm, pretrained, **kwargs)
RCF Head
RCF 边缘检测头
class RCFHead(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self,
fea_channels=[64, 128, 256, 512, 512],
fea_nums=[2, 2, 3, 3, 3],
hidden_dim=21
):
Head of RCF model\nPaper: Richer Convolutional Features for Edge Detection\n Link: http://mftp.mmcheng.net/Papers/19PamiEdge.pdf
param:
fea_channels(List[int]): channels of the input features from the backbonefea_nums(List[int]): the num of features each stage hidden_dim(int: 21): hidden dim
super().__init__()
self.head_downs = nn.LayerList()
self.head_score = nn.LayerList()
for feas_channel, fea_num in zip(fea_channels, fea_nums):
downs = nn.LayerList()
for _ in range(fea_num):
down = nn.Conv2D(in_channels=feas_channel, out_channels=hidden_dim, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
downs.append(down)
self.head_downs.append(downs)
score = nn.Conv2D(in_channels=hidden_dim, out_channels=1, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
self.head_score.append(score)
self.head_weight = nn.Conv2D(in_channels=len(fea_channels), out_channels=1, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
def forward(self, fea_inputs):
RCFHead forward func
param:
fea_inputs(List[List[Tensor]]): input features from the backbone return:
outputs(List[Tensor]): outputs of each stages and weight output
h, w = fea_inputs[0][0].shape[2:]
outputs = []
for i, (fea_input, score_layer) in enumerate(zip(fea_inputs, self.head_score)):
down_outputs = []
for fea, down_layer in zip(fea_input, self.head_downs[i]):
down_output = down_layer(fea)
down_outputs.append(down_output)
fea_input = paddle.add_n(down_outputs)
score_output = score_layer(fea_input)
if i > 0:
# score_output = F.upsample(score_output, size=(h, w), mode=bilinear)
score_output = F.conv2d_transpose(score_output, self.bilinear_kernel(1, 1, 2**(i+1)), stride=2**(i))
h_, w_ = score_output.shape[2:]
score_output = score_output[:, :, (h_-h)//2:(h_-h)//2+h, (w_-w)//2: (w_-w)//2+w]
outputs.append(score_output)
concat_outputs = paddle.concat(outputs, 1)
weight_outputs = self.head_weight(concat_outputs)
outputs.append(weight_outputs)
return outputs
@staticmethod
def bilinear_kernel(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size):
return a bilinear filter tensor
factor = (kernel_size + 1) // 2
if kernel_size % 2 == 1:
center = factor - 1
else:
center = factor - 0.5
og = np.ogrid[:kernel_size, :kernel_size]
filt = (1 - abs(og[0] - center) / factor) * (1 - abs(og[1] - center) / factor)
weight = np.zeros((in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, kernel_size), dtype=float32)
weight[range(in_channels), range(out_channels), :, :] = filt
return paddle.to_tensor(weight, dtype=float32)
RCF 模型
class RCF(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self, pretrained=False, backbone_pretrained=False):
The base class of the models
params:
backbone(Layer): the backbone of the model like VGG head(Layer): the head of the model
super().__init__()
self.backbone = vgg16(
pretrained=backbone_pretrained,
return_idx=[[0, 1], [2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9], [10, 11, 12]]
)
self.head = RCFHead(
fea_channels=[64, 128, 256, 512, 512],
fea_nums=[2, 2, 3, 3, 3],
hidden_dim=21,
)
if pretrained:
params = paddle.load(rcf_pretrained_bsds.pdparams)
self.set_dict(params)
def forward(self, inputs):
Base model forward func params:
inputs(Tensor): the input Tensor.
return:
outputs(List[Tensor]): outputs of each stages and weight output
outputs = self.backbone(inputs)
outputs = self.head(outputs)
return outputs
数据预处理
def preprocess(img):
img = img.astype(float32)
img -= np.asarray([104.00698793, 116.66876762, 122.67891434], dtype=float32)
img = img.transpose(2, 0, 1)
img = img[None, ...]
return paddle.to_tensor(img, dtype=float32)
结果后处理
def postprocess(outputs):
results = F.sigmoid(outputs)
results = paddle.squeeze(results, 1)
results *= 255.0
results = results.cast(uint8)
return results.numpy()
模型推理
model = RCF(pretrained=True)
img = cv2.imread(sample.png)
img_tensor = preprocess(img)
outputs = model(img_tensor)
results = postprocess(outputs[-1])
show_img = np.concatenate([cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB), cv2.cvtColor(results[0], cv2.COLOR_GRAY2RGB)], 1)
Image.fromarray(show_img)
模型训练
至于模型训练的部分和 HED 一样(咕咕咕)
后续会有个项目来介绍如何训练(快搞完了,真的^_^)
总结
RCF 是 CVPR 2017 上发表的论文,相比两年前的 HED 模型,可以看出很多相似的地方
其中主要的提升点在于使用了更多层级的卷积特征图融合后进行边缘检测,进一步提高了模型的效果
此系列尚未完结,后续还有更加前沿的模型即将登场